GtdProviderGtdProvider — data sources for GNOME To do |
Stability Level
Developers of the free and open-source 'Getting Things GNOME' GTD desktop application are asking for feedback on what matters most to users, and want to see if how much demand there is for this app to continue being maintained. As far as I know, it's the only well-designed, graphical, free and open-source, GTD-focused app out there. GTG is an application made and tested on Linux-based OSes (like Fedora and Ubuntu). Some rumors say it works on.BSD, but we're pretty sure it does not work on Windows (because none of us run that). We're developing GTG to make our lives more pleasant and productive on Linux, not to compete with the plethora of proprietary GTD apps out there. (GTG) is a personal tasks and TODO list items organizer for the GNOME desktop environment inspired by the Getting Things Done (GTD) methodology. GTG is designed with flexibility, adaptability, and ease of use in mind so it can be used as more than just GTD software.
Unstable, unless otherwise indicatedFunctions
| const gchar * | gtd_provider_get_id() |
| const gchar * | gtd_provider_get_name() |
| const gchar * | gtd_provider_get_description() |
| gboolean | gtd_provider_get_enabled() |
| GIcon * | gtd_provider_get_icon() |
| const GtkWidget * | gtd_provider_get_edit_panel() |
| void | gtd_provider_create_task() |
| void | gtd_provider_update_task() |
| void | gtd_provider_remove_task() |
| void | gtd_provider_create_task_list() |
| void | gtd_provider_update_task_list() |
| void | gtd_provider_remove_task_list() |
| GList * | gtd_provider_get_task_lists() |
| GtdTaskList * | gtd_provider_get_default_task_list() |
Properties
| GtdTaskList * | default-task-list | Read / Write |
| gchar * | description | Read |
| gboolean | enabled | Read |
| GIcon * | icon | Read |
| gchar * | id | Read |
| gchar * | name | Read |
Signals
| void | list-added | Run Last |
| void | list-changed | Run Last |
| void | list-removed | Run Last |
Types and Values
| #define | GTD_TYPE_PROVIDER |
| struct | GtdProviderInterface |
| GtdProvider |
Prerequisites
GtdProvider requires GtdObject.
Description
The GtdProvider is the interface that GNOME To Do uses toconnect to data sources. It must provide ways to create, updateand remove tasks and tasklists.
A provider implementation must also expose which is the defaulttasklist among the tasklists it manages.
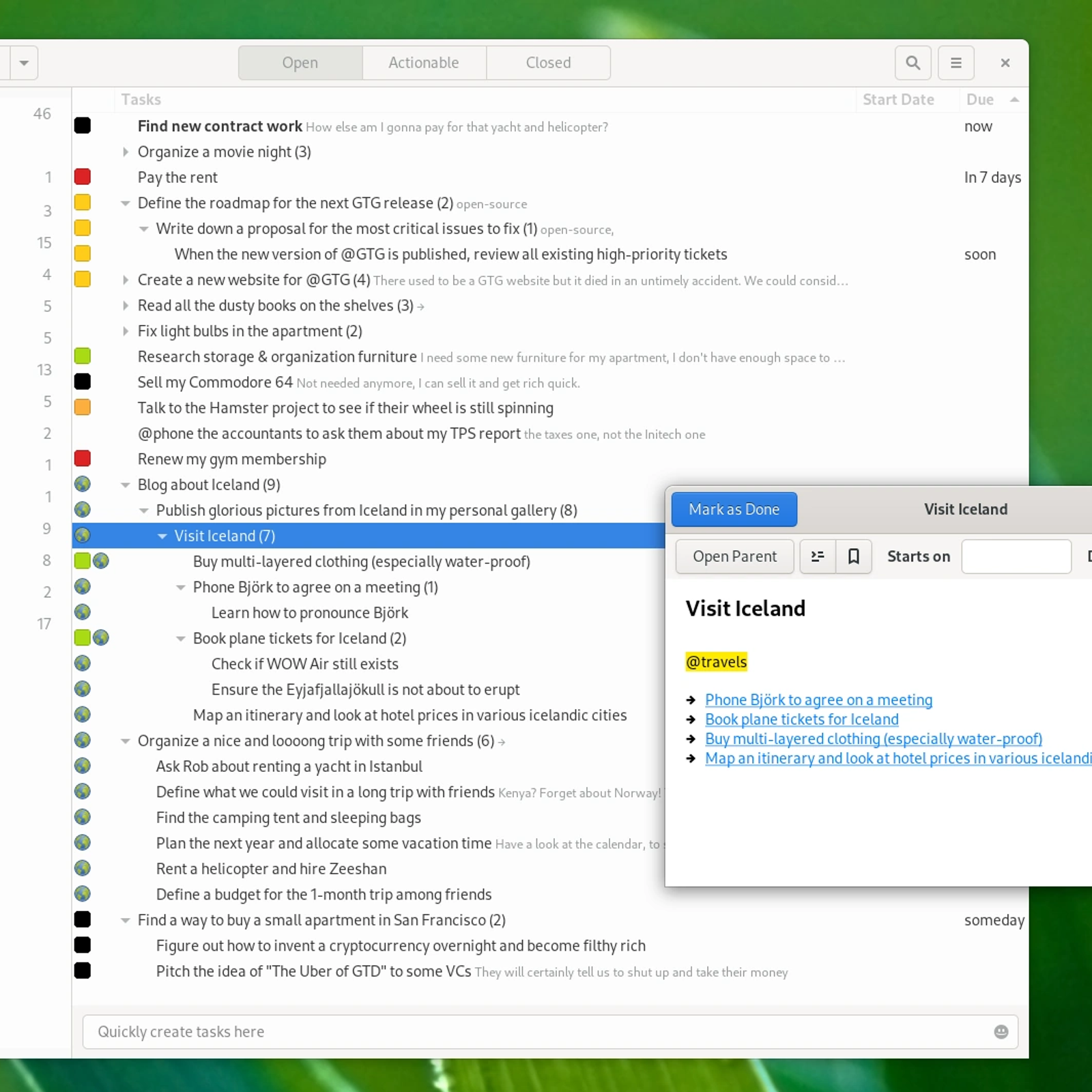
Functions
gtd_provider_get_id ()
Retrieves the identifier of provider.
Parameters
Returns
the id of provider.
[transfer none]
gtd_provider_get_name ()
Retrieves the user-visible name of provider.
Parameters
Returns
the name of provider.
[transfer none]
gtd_provider_get_description ()
Retrieves the description of provider.
Parameters
Returns
the description of provider.
Gnome Gtk
[transfer none]
gtd_provider_get_enabled ()
Retrieves whether provider is enabled or not. A disabledprovider cannot be selected to be default nor be selectedto add tasks to it.
Parameters
Returns
TRUE if provider is enabled, FALSE otherwise.
gtd_provider_get_icon ()
The icon of provider.
Parameters
Returns
a GIcon.
[transfer none]
gtd_provider_create_task ()
Creates the given task in provider.
Parameters
gtd_provider_update_task ()
Updates the given task in provider.
Parameters
gtd_provider_remove_task ()
Removes the given task from provider.
Parameters
gtd_provider_create_task_list ()
Creates the given list in provider.
Parameters
gtd_provider_update_task_list ()
Updates the given list in provider.
Parameters
gtd_provider_remove_task_list ()
Removes the given list from provider.

Parameters

gtd_provider_get_task_lists ()
Retrieves the tasklists that this provider contains.
Parameters
Returns
the list of tasks, or NULL.
[transfer container][element-type Gtd.TaskList]
gtd_provider_get_default_task_list ()
Retrieves the default tasklist of provider.
Parameters
Returns
the default tasklist, or NULL.
[transfer none][nullable]
Types and Values
struct GtdProviderInterface
Property Details
The “default-task-list” property
The default tasklist of the provider.
Flags: Read / Write
The “description” property
The description of the provider.
Flags: Read
Default value: NULL
The “enabled” property
The identifier of the provider.
Flags: Read
Default value: FALSE
The “icon” property
The icon of the provider.
Flags: Read
The “id” property
The identifier of the provider.
Flags: Read
Default value: NULL
The “name” property
The user-visible name of the provider.
Flags: Read
Default value: NULL
Signal Details
The “list-added” signal
The ::list-added signal is emmited after a GtdTaskListis connected.
Parameters
provider | a GtdProvider |
list | a GtdTaskList |
user_data | user data set when the signal handler was connected. |
Gnome Gtk3
Flags: Run Last
The “list-changed” signal
The ::list-changed signal is emmited after a GtdTaskListhas any of it's properties changed.
Parameters
provider | a GtdProvider |
list | a GtdTaskList |
user_data | user data set when the signal handler was connected. |
Flags: Run Last
The “list-removed” signal
The ::list-removed signal is emmited after a GtdTaskListis disconnected.
Parameters
provider | a GtdProvider |
list | a GtdTaskList |
user_data | user data set when the signal handler was connected. |
Flags: Run Last
Getting Things Done: The Art of Stress-Free Productivity cover, first edition | |
| Author | David Allen |
|---|---|
| Subject | Business |
| Publisher | Penguin Books |
| 2001 | |
Published in English | 2001 |
| Pages | 267 |
| ISBN | 978-0-14-312656-0 (2015 Reprint Edition) |
| OCLC | 914220080 |
Getting Things Done (GTD) is a process for increasing your own productivity. In his book the author states that it is not a time management system but instead is a process for bringing order and action to our typically chaotic and random individual worlds. The system and process for achieving this is described in the book of the same title[1] by productivity consultant David Allen.
The GTD method rests on the idea of moving all items of interest, relevant information, issues, tasks and projects out of the mind by recording them externally and then breaking them into actionable work items. This allows attention to be focused on taking action on tasks, instead of recalling them.[2]
First published in 2001, a revised edition of the book was released in 2015 to reflect the changes in information technology during the preceding decade.
Themes[edit]
Allen first demonstrates stress reduction from the method with the following exercise, centered on a task that has an unclear outcome or whose next action is not defined. Allen calls these sources of stress 'open loops', 'incompletes', or 'stuff'.[1]:13
- The most annoying, distracting, or interesting task is chosen, and defined as an 'incomplete'.
- A description of the successful outcome of the 'incomplete' is written down in one sentence, along with the criteria by which the task will be considered completed.
- The next step required to approach completion of the task is written down.
- A self-assessment is made of the emotions experienced after completing the steps of this process.
He claims stress can be reduced and productivity increased by putting reminders about everything you are not working on into a trusted system external to your mind. In this way, you can work on the task at hand without distraction from the 'incompletes'.[1]:14 The system in GTD requires you to have the following tools within easy reach:
- An inbox
- A trash can
- A filing system for reference material
- Several lists (detailed below)
- A calendar.
These tools can be physical or electronic as appropriate (e.g., a physical 'in' tray or an email inbox).[1]:88 Then, as 'stuff' enters your life, it is captured in these tools and processed with the following workflow.[1]:27
Workflow[edit]
The GTD workflow consists of five stages: capture, clarify, organize, reflect, and engage.[3] (The first edition used the names collect, process, organize, plan, and do; the descriptions of the stages are similar in both editions). Once all the material ('stuff') is captured (or collected) in the inbox,[1]:106 each item is clarified[1]:122 and organized[1]:141 by asking and answering questions about each item in turn as shown in the black boxes in the logic tree diagram. As a result, items end up in one of the eight oval end points in the diagram:
- in the trash
- on the someday/maybe list
- in a neat reference filing system
- on a list of tasks, with the outcome and next action defined if the 'incomplete' is a 'project' (i.e., if it will require two or more steps to complete it)
- immediately completed and checked off if it can be completed in under two minutes
- delegated to someone else and, if you want a reminder to follow up, added to a 'waiting for' list
- on a context-based 'next action' list if there is only one step to complete it
- on your calendar[1]:27
Empty your inbox or inboxes daily or at least weekly ('in' to empty).[1]:122 Don't use your inbox as a 'to do' list. Don't put clarified items back into the inbox.[1]:27 Emptying your inbox doesn't mean finishing everything. It just means applying the 'capture, clarify, organize' steps to all your 'stuff'.[1]:27
Next, reflection (termed planning in the first edition) occurs. Multi-step projects identified above are assigned a desired outcome and a single 'next action'.[1]:191 Finally, a task from your task list is worked on ('engage' in the 2nd edition, 'do' in the 1st edition) unless the calendar dictates otherwise. You select which task to work on next by considering where you are (i.e., the 'context', such as at home, at work, out shopping, by the phone, at your computer, with a particular person), time available, energy available, and priority.[1]:204
Implementation[edit]
Because hardware and software is changing so rapidly, GTD is deliberately technologically-neutral. (In fact, Allen advises people to start with a paper-based system.[4]) Many task management tools claim to implement GTD methodology[5] and Allen maintains a list of some technology that has been adopted in or designed for GTD. Some are designated 'GTD Enabled', meaning Allen was involved in the design.[6]
Perspective[edit]
Allen emphasizes two key elements of GTD — control and perspective. The workflow is the center of the control aspect. The goal of the control processes in GTD is to get everything except the current task out of your head and into this trusted system external to your mind. He borrows a simile used in martial arts termed 'mind like water'. When a small object is thrown into a pool of water, the water responds appropriately with a small splash followed by quiescence. When a large object is thrown in the water again responds appropriately with a large splash followed by quiescence. The opposite of 'mind like water' is a mind that never returns to quiescence but remains continually stressed by every input.[1]:12 With a trusted system and 'mind like water' you can have a better perspective on your life. Allen recommends reflection from six levels, called 'Horizons of Focus':[1]:215–219
- Horizon 5: Life
- Horizon 4: Long-term visions
- Horizon 3: 1-2 year goals
- Horizon 2: Areas of focus and accountability
- Horizon 1: Current projects
- Ground: Current actions
Unlike some theories, which focus on top-down goal-setting, GTD works in the opposite direction. Allen argues that it is often difficult for individuals to focus on big picture goals if they cannot sufficiently control the day-to-day tasks that they frequently must face.[1]:54 By developing and using the trusted system that deals with day-to-day inputs, an individual can free up mental space to begin moving up to the next level.[citation needed]
Allen recommends scheduling a weekly review, reflecting on the different levels. The perspective gained from these reviews should drive one's priorities at the project level.[1]:50 Priorities at the project level in turn determine the priority of the individual tasks and commitments gathered during the workflow process. During a weekly review, determine the context for the tasks and put each task on its appropriate list. An example of grouping together similar tasks would be making a list of outstanding telephone calls, or the tasks/errands to perform while out shopping. Context lists can be defined by the set of tools available or by the presence of individuals or groups for whom one has items to discuss or present.[citation needed]
Gnome Gdm Theme
Summary[edit]
GTD is based on storing, tracking, and retrieving the information related to the things that need to get done. Mental blocks we encounter are caused by insufficient 'front-end' planning. This means thinking in advance, generating a series of actions which can later be undertaken without further planning. The mind's 'reminder system' is inefficient and seldom reminds us of what we need to do at the time and place when we can do it. Consequently, the 'next actions' stored by context in the 'trusted system' act as an external support which ensures that we are presented with the right reminders at the right time. As GTD relies on external reminders, it can be seen as an application of the theories of distributed cognition or the extended mind.[7]
Reception[edit]
In 2005, Wired called GTD a 'new cult for the info age',[8] describing the enthusiasm for this method among information technology and knowledge workers as a kind of cult following. Allen's ideas have also been popularized through the Howard Stern Show (Stern referenced it daily throughout 2012's summer) and the Internet, especially via blogs such as 43 Folders,[9]Lifehacker,[10] and The Simple Dollar.[11]

In 2005, Ben Hammersley interviewed David Allen for The Guardian article titled 'Meet the man who can bring order to your universe',[12] saying: 'For me, as with the hundreds of thousands around the world who press the book into their friends' hands with fire in their eyes, Allen's ideas are nothing short of life-changing'.
In 2007, Time Magazine called Getting Things Done the self-help business book of its time.[13]
In 2007, Wired ran another article about GTD and Allen,[14] quoting him as saying 'the workings of an automatic transmission are more complicated than a manual transmission... to simplify a complex event, you need a complex system'.
A paper in the journal Long Range Planning by Francis Heylighen and Clément Vidal of the Free University of Brussels showed 'recent insights in psychology and cognitive science support and extend GTD's recommendations'.[7]
See also[edit]
Gnome Gtk Theme
References[edit]
Gnome Gdk
- ^ abcdefghijklmnopqrAllen, David (2015). Getting Things Done: The Art of Stress-Free Productivity (2 ed.). Penguin Books. ISBN9780143126560.
- ^Fallows, James (November 2012). 'Busy and Busier'. The Atlantic. Retrieved December 28, 2018.
- ^David Allen (2001). 'Getting Things Done: Five Simple Steps That Apply Order To Chaos'. gettingthingsdone.com. Retrieved 2019-07-27.
- ^Forrister, Kelly (2010-08-02). 'Which list manager should I use for GTD?'. GTD Times. The David Allen Company. Archived from the original on 2010-08-06. Retrieved 2015-01-04.
- ^Forrister, Kelly (2009-05-04). 'Simply GTD with Kelly: Getting Started'. The David Allen Company. Archived from the original on 2010-08-29. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
If you're at all familiar with GTD you know that David Allen does not tell you which tools to use--GTD is tool agnostic--so those choices are up to you. Not saying all tools, software programs, paper planners work seamlessly with GTD, but where you organize your stuff is up to you.
- ^'Common Tools & Software'. Getting Things Done website. David Allen Co. Retrieved 2014-05-30.
- ^ abHeylighen, Francis; Vidal, Clément (December 2008). 'Getting Things Done: The Science behind Stress-Free Productivity'(PDF). Long Range Planning: International Journal of Strategic Management. 41 (6): 585–605. CiteSeerX10.1.1.161.441. doi:10.1016/j.lrp.2008.09.004. ISSN0024-6301.
- ^Andrews, Robert (2005-07-12). 'A new cult for the info age'. Wired.com. Condé Nast. Retrieved 2020-05-02.
- ^Mann, Merlin (2004-09-08). 'Getting started with 'Getting Things Done''. 43 Folders. Retrieved 2020-05-02.
- ^Robinson, Keith (2006-03-21). 'Best of GTD'. Lifehacker. Retrieved 2020-05-02.
- ^'Review: Getting Things Done'. The Simple Dollar. 2020-04-09. Retrieved 2020-05-02.
- ^Hammersley, Ben (2005-09-28). 'Meet the man who can bring order to your universe'. The Guardian. London: Guardian News and Media Limited. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^'The Oracle of Organization'. Time. 2007-03-12. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^Wolf, Gary (2007-09-25). 'Getting Things Done Guru David Allen and His Cult of Hyperefficiency'. Wired.com. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
Gnome Gdm
Further reading[edit]
- Allen, David (2001). Getting Things Done: The Art of Stress-Free Productivity (1 ed.). Penguin Books. ISBN978-0-14-200028-1.
- Allen, David (2003). Ready for Anything: 52 Productivity Principles for Work and Life. Viking Books. ISBN978-0-670-03250-1.
- Allen, David (2008). Making it All Work. Viking Books. ISBN978-0-7499-4103-1.